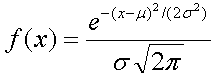
f(x) = height of the normal curve on the vertical axis for a value x
x = a value on the horizontal axis
μ = mean of the normal distribution
σ = standard deviation of the normal distribution
π = 3.14159… (mathematical constant)
e = 2.71828… (mathematical constant)
If we know the mean, μ, and standard deviation, σ, for a normal distribution, then we know everything about the distribution. We can compute the probability of observing an x score above or below any specific value. Fortunately, tables and computer programs are available to help us find these values.
![]()

